A web server requires an SSL Certificate to establish a secure connection. To enable SSL on your server, select the appropriate SSL type based on your needs. This KB will highlight the key distinctions between SSL types.
1) What is SSL Certificate?
SSL/TLS certificates are very important in online security. SSL (Secure Socket Layer) is being used by millions of websites to protect online transactions. SSL works as an encrypted link between a web server and a web browser. With cybercrime on the rise, utilizing SSL/TLS certificates is critical to establishing user confidence and progressing toward greater digital security. SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificates are a validation and encryption mechanism used as part of the HTTPS protocol to secure and encrypt data.
2) Types of SSL
There are three types of SSL Certificates:
- Single-Domain SSL
- Multi-Domain SSL
- Wildcard SSL
- Single-Domain SSL
Single-Domain SSL Certificate(s) can only be used on one specific website or one fully qualified domain name (FQDN). When a certificate has only one SAN field and a reference to a single website, it is referred to as a single-domain certificate such as “mywebsite.com” or “new.mywebsite.com.”
For example, if you purchase www.mywebsite.com or mywebsite.com, it will also cover NON-WWW or WWW domain but NOT any other sub-domain such as new.mywebsite.com. It simply refers to the Subject Alternative Name (SAN) field, which is contained in the certificate when it is issued. The single-domain SSL support both www and non-www URLs, for example, https://mywebsite.com and https://www.mywebsite.com but some SSL certificate issuer doesn’t support single-domain SSL on both URL’s(www and non-www), so make sure when you purchase the single-domain SSL it will support www and non-www URL.

- Multi-Domain SSL
The use of a single SSL certificate is to manage the security features of several domain names easily and cost-effectively. Multi-Domain SSL is also known as Subject Alternative Name (SAN) and Unified Communication Certificate (UCC). A Multi-Domain SSL protects several Fully Qualified Domain Names (FQDN), which can be a top-level domain or a subdomain with a single certificate. Multi-Domain SSL can secure multiple primary domains as well as multiple sub-domains. The maximum number of domains that may be secured with a single SSL certificate is 250.
Below are the examples of the Multi-Domain SSL Certificate:
- www.site1.com
- www.test.com
- www.site2.com
- new.site1.com
- new.site2.com
- www.site1.org
- www.site2.net

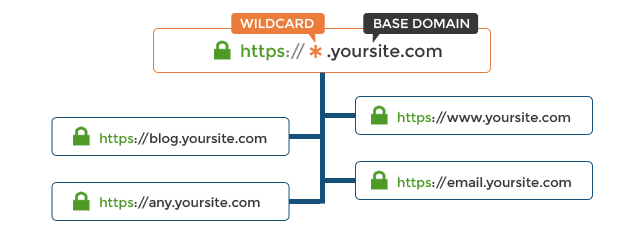
- Wildcard SSL
Users can get a certificate for a single domain using Wildcard SSL. They may, however, protect numerous subdomains inside the parent domain. The user must acquire an SSL certificate for the parent domain, and all subdomains are covered automatically. A wildcard SSL issued for *.domain.com, for example, would secure blog.domain.com, store.domain.com, www.domain.com, and so on.
Users can protect an unlimited number of subdomains, but only one primary domain. They must obtain numerous different certificates if they wish to secure several domains (or get a multi-domain wildcard SSL).
3) Difference of Single, Multiple, and Wildcard SSL
Single-Domain SSL | Multi-Domain SSL | Wildcard SSL |
Certificate for one domain name. | Single certificate for multiple domain names. | Single certificate for unlimited sub-domain names of one primary domain. |
mywebsite.com | mywebsite.com, mywebsite.net, mywebsite1845.com | Shop.mywebsite.com, blog. mywebsite.com, live. mywebsite.com |
DV, OV, and EV are all levels of validation supported. | DV, OV, and EV are all levels of validation supported. | Only DV and OV levels of validation are supported. Not EV validation supported. |
Only one domain name is supported. | Number of domain name supported depend on CA or generally 250 domain names. | Unlimited sub-domain covered. |
Only one domain name covered, which was defined during certificate issuance. | All domain names secured, which was defined during certificate issuance. | Any sub-domain name can be added or removed at any time. |
Support www and non-www URL’s. | Support www and non-www URL’s. | Support www by the asterisk (“*”) and non-www also supported. |
Issued Immediately. | Issuance Time-Period more than 3 Days. | Issuance Time-Period more than 10 Days. |
4) What are DV, OV, and EV validation?
Before moving further, let’s understand some abbreviation that is very important while deciding to purchase an SSL certificate.
DV stands for Domain Verification SSL Certificate are issued when the certificate authority checks to make sure that the applicant has the right or ownership of domain name. The company identification is not verified during certificate issuance, and the DV certificate can be issued immediately.
OV stands for Organization Validation SSL Certificate, a high assurance SSL certificate used to validate a company or business. The certificate issuance authority verifies an organization or business, and the applicant must provide the acceptable business prove document to the certificate authority during certificate issuance.
The additional verified company information is displayed to the customer when the user clicks the secure seal or secure lock or browser URL bar. This gives an enhanced trust to the user on the company or website. Usually, the OV SSL certificate takes three days to issue.
EV stands for Extended Validation SSL Certificate issued only when certificate authority verifies that the applicant has the right to the domain name plus CA conduct an organization investigation and verification check in detail as per the guidelines mentioned in the EV Guidelines, which was created in 2007 at the CA/Browser Forum. The summary of the main points of EV Guidelines mention below.
- Applicant must provide the required documentation to verify the legal, physical and operational existence of the business.
- Must provide the document to identify the business matches official records.
- Complete the domain name authentication process, and the domain name matches the organization name also registered with ICANN or an IANA registrar.
- Must verify that the domain name and business have properly authorized the issuance and use of the EV Certificate.
- Telephonic verification is also required.
EV certificates are issued and used by all types of organizations, and it takes more than 10 days to issue.
5) Which SSL Certificate is right for you?
The use of an SSL certificate depends on your requirement. If you have only one domain name and don’t plan to add any sub-domain and other domain names, then a single SSL certificate is a cost-effective and right decision with full security coverage.
If you have many domain names and want full security coverage with cost-effective and easy management solutions, then Multi-Domain SSL is a good choice for you.
The wildcard SSL certificate usage is a little bit difficult if your organization or business want EV validation because wildcard certificate gives you full coverage of unlimited sub-domain name of one primary domain name without EV validation. If you don’t want EV validation and you have a different sub-domain related to single primary domain name in use, then wildcard SSL is the best choice in this case.

